What You Should Know:
– Public cloud providers are increasingly important to how HIT vendors deliver software to provider and payer organizations.
– To help HIT vendors make informed decisions about which public cloud provider can best meet their needs, a new report from KLAS examines (1) how industry adoption of public cloud solutions is progressing and (2) how well public cloud providers perform in key areas, including their strengths and improvement opportunities
Vital Trends and Insights From Public Cloud Providers 2022
Each year, KLAS interviews thousands of healthcare professionals about the IT solutions and services their organizations use.
This latest report uniquely reports on a different set of customers: HIT software vendors as clients of public cloud providers. For this study, KLAS created a supplemental evaluation (rather than a standard evaluation, administered to healthcare providers and payer organizations) to delve deeper into several questions specific to the public cloud provider market and vendors’ experiences as clients of cloud providers. This evaluation asked respondents (1) why they selected their cloud provider, (2) where they are at in their cloud journey, (3) the benefits and obstacles of their cloud solution, and (4) what priorities cloud providers should address.
Key trends and insights from the report are listed and explained as follows:
1. HIT Vendors Making Rapid Progress with Cloud Solutions
Nearly half of interviewed vendors have migrated all their go-forward solutions to the cloud, and nearly all of the rest are in various phases of implementation or migration. Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the most widely used primary cloud provider. Microsoft Azure is gaining ground with recent wins—75% of interviewed vendors who are in early phases of moving to the cloud are using Microsoft Azure as their primary cloud provider. Approaches to migrating include refactoring applications, cloud-native development, leveraging containers, lift- and-shift of legacy solutions, and back-end enhancements. Almost half of interviewed vendors have made their go-forward products commercially available in the cloud. Among these, about three-quarters have products running in a multi-tenant SaaS environment; the rest run their products in a single-tenant SaaS environment or have created platform-based offerings that allow clients to use their cloud provider of choice. Many vendors that previously had legacy solutions have either replaced or refactored their products, and they are still transitioning clients to the cloud. About one-third of interviewed vendors use multiple cloud providers. Reasons for this include the desire to accommodate payer/provider clients’ cloud preferences, the acquisition of products hosted by a different cloud provider, and functionality gaps. Vendors who use Microsoft Azure as their primary cloud provider are twice as likely as AWS clients to use a secondary cloud provider.
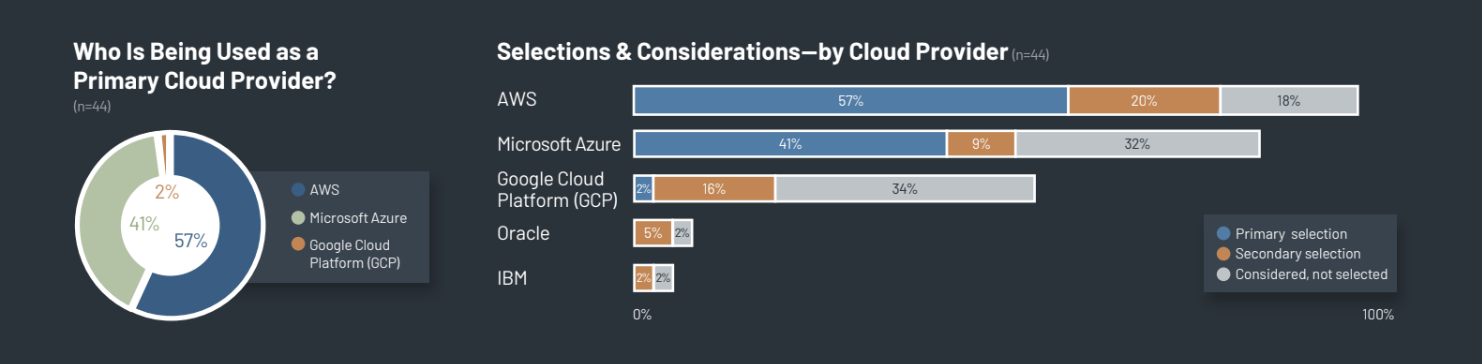
2. AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud – The Race
AWS is most often considered and implemented—over 95% of interviewed vendors considered AWS, and nearly 80% use AWS as a primary or secondary cloud provider. The 57% of respondents using AWS as their primary cloud provider cite the company ’s experience and mature technology. Additionally, AWS was the first to provide public cloud services, giving them many early considerations. Microsoft Azure is gaining momentum, with maturing cloud capabilities that several vendors describe as comparable to AWS ’. Over 80% of respondents considered Microsoft Azure, and more than half use them as a primary or secondary cloud provider. Those using Microsoft Azure as their primary cloud provider frequently mention established relationships with Microsoft, software bundling, and favorable pricing as key factors. Google Cloud Platform (GCP) was considered by about half of interviewed vendors and is currently used by one interviewed vendor as a primary cloud provider; GCP is used more often as a secondary cloud provider to fill functionality gaps or enhance capabilities.
3. Analysing Microsoft Azure’s Healthcare Expertise, AWS’ Value, and GCP Playing Catch Up
Cloud providers perform similarly well in terms of technology, security, and operational resilience. Microsoft Azure leads among cloud providers for ease of integration and healthcare expertise. Vendors appreciate the broad offering and strong integration tools and documentation. Microsoft’s solid expertise is supported by industry-experienced staff, deep relationships with health systems, and significant investment in healthcare (though room for improvement remains). Cost and value are weaker points for Microsoft; despite software bundling and volume discounts, some clients report costs can be difficult to predict and manage. AWS leads the market in cost and value. Vendors say AWS proactively works with them to reduce costs as much as possible; predicting and managing costs can still be challenging. Integration with other AWS clients is easy thanks to AWS’ flexibility and simple configurations. Improvement is needed around healthcare expertise; several respondents noted AWS seems more focused on technology than healthcare. A few vendors express excitement around recent AWS investments in the healthcare market and hope AWS’ focus will shift more toward healthcare. GCP is rated lowest for most areas. Vendors appreciate GCP’s competitive pricing and white-glove approach with new customers. The main complaints include not enough flexibility with non-Google tools, high costs for nonproduction environments, and a more technical focus. Some respondents are encouraged by recent healthcare investments.
4. Support Gaps and Cost Management As Obstacles
Support gaps and cost management are often-mentioned obstacles that interviewed vendors encounter with cloud providers. Vendors primarily using AWS ’ cloud solution cite challenges with account turnover, navigating AWS ’ organization, and a lack of visibility into technical issues. These vendors also describe billing as complex and say costs quickly get out of control if not watched closely—one AWS client noted it can be confusing to understand the cost of running the entire IT environment, the transition costs, and the discounting programs. Additionally, customers struggle with the rapid pace of change with AWS ’ constant innovations. Vendors primarily using Microsoft Azure’s cloud note challenges navigating Microsoft’s organization and accessing resources who can solve complex problems. Understanding and managing costs is also a frequently mentioned obstacle. One Microsoft customer shared that there is sometimes a lack of alignment between what representatives are incentivized to do and what customers would most benefit from. Some Microsoft Azure clients also report learning curve challenges because they don’t have enough people familiar with the Azure environment and struggle to recruit and train people with needed expertise.
5. Cost, Products Enhancements and Security Are Top Priorities For Future Vendor Focus:
HIT vendors still face many challenges that make moving to the cloud difficult. Cost is the most frequently mentioned challenge. Respondents cite storage- retrieval and egress fees, and they would like billing to be simplified and cost-management tools to be improved. Vendors also want to see continual, faster investment from cloud providers in core solutions so they can increase adoption. Desired investments include better tool standardization, a scalable and relational database, more base features and AI capabilities, and better monitoring tools. Additionally, respondents note cloud providers should take on more risk related to security. Vendors want help with ransomware, more security certification coverage, upstream safeguards, better authorization and access, and less traditional IT infrastructure in the cloud.
