What You Should Know:
– NVIDIA and Massachusetts General Brigham Hospital researchers develop an AI model that determines whether a person showing up in the emergency room with COVID-19 symptoms will need supplemental oxygen hours or even days after an initial exam.
– The ultimate goal of this model is to predict the likelihood that a person showing up in the emergency room will need supplemental oxygen, which can aid physicians in determining the appropriate level of care for patients, including ICU placement.
Researchers at NVIDIA and Massachusetts General Brigham Hospital have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) model that determines whether a person showing up in the emergency room with COVID-19 symptoms will need supplemental oxygen hours or even days after an initial exam.
The original AI model, named CORISK, was developed by scientist Dr. Quanzheng Li at Mass General Brigham. It combines medical imaging and health records to help clinicians more effectively manage hospitalizations at a time when many countries may start seeing the second wave of COVID-19 patients.
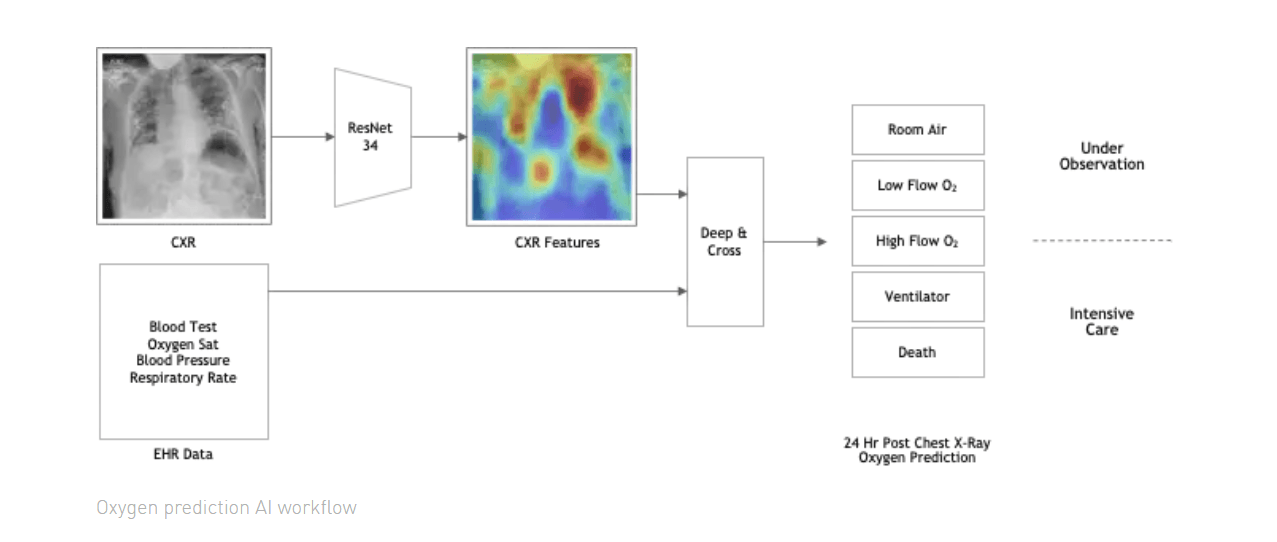
EXAM (EMR CXR AI Model) & Results
To develop an AI model that doctors trust and that generalizes to as many hospitals as possible, NVIDIA and Mass General Brigham embarked on an initiative called EXAM (EMR CXR AI Model) the largest, most diverse federated learning initiative with 20 hospitals from around the world.
In just two weeks, the global collaboration achieved a model with .94 area under the curve (with an AUC goal of 1.0), resulting in excellent prediction for the level of oxygen required by incoming patients. The federated learning model will be released as part of NVIDIA Clara on NGC in the coming weeks.
Leveraging NVIDIA’s Clara Federated Learning Framework
Using NVIDIA Clara Federated Learning Framework, researchers at individual hospitals were able to use a chest X-ray, patient vitals and lab values to train a local model and share only a subset of model weights back with the global model in a privacy-preserving technique called federated learning.
The ultimate goal of this model is to predict the likelihood that a person showing up in the emergency room will need supplemental oxygen, which can aid physicians in determining the appropriate level of care for patients, including ICU placement.
Dr. Ittai Dayan, who leads the development and deployment of AI at Mass General Brigham, co-led the EXAM initiative with NVIDIA and facilitated the use of CORISK as the starting point for the federated learning training. The improvements were achieved by training the model on distributed data from a multinational, diverse dataset of patients across North and South America, Canada, Europe, and Asia.
Participating Hospitals in EXAM Initiative
In addition to Mass Gen Brigham and its affiliated hospitals, other participants included: Children’s National Hospital in Washington, D.C.; NIHR Cambridge Biomedical Research Centre; The Self-Defense Forces Central Hospital in Tokyo; National Taiwan University MeDA Lab and MAHC and Taiwan National Health Insurance Administration; Kyungpook National University Hospital in South Korea; Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University in Thailand; Diagnosticos da America SA in Brazil; University of California, San Francisco; VA San Diego; University of Toronto; National Institutes of Health in Bethesda, Maryland; University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Medicine and Public Health; Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York; and Mount Sinai Health System in New York.
Each of these hospitals used NVIDIA Clara to train its local models and participate in EXAM. Rather than needing to pool patient chest X-rays and other confidential information into a single location, each institution uses a secure, in-house server for its data. A separate server, hosted on AWS, holds the global deep neural network, and each participating hospital gets a copy of the model to train on its own dataset.
NVIDIA Announces Partnership with GSK’s AI-Powered Lab for Discovery of Medicines and Vaccines
In addition, the new AI model, NVIDIA today announced a partnership with global healthcare company GSK and its AI group, which is applying computation to the drug and vaccine discovery process. GSK has recently established a new London-based AI hub, one of the first of its kind, which will leverage GSK’s significant genetic and genomic data to improve the process of designing and developing transformational medicines and vaccines.
Located in London’s rapidly growing Knowledge Quarter, GSK’s hub will utilize biomedical data, AI methods, and advanced computing platforms to unlock genetic and clinical data with increased precision and scale. The GSK AI hub, once fully operational, will be home to its U.K.-based AI team, including GSK AI Fellows, a new professional training program, and now scientists from NVIDIA.
NVIDIA Building UK’s Most Powerful Supercomputer, Dedicated to AI Research in Healthcare

NVIDIA today announced that it is building the United Kingdom’s most powerful supercomputer, which it will make available to U.K. healthcare researchers using AI to solve pressing medical challenges, including those presented by COVID-19.
Expected to come online by year end, the “Cambridge-1” supercomputer will be an NVIDIA DGX SuperPOD™ system capable of delivering more than 400 petaflops of AI performance and 8 petaflops of Linpack performance, which would rank it No. 29 on the latest TOP500 list of the world’s most powerful supercomputers. It will also rank among the world’s top 3 most energy-efficient supercomputers on the current Green500 list.
