What You Should Know:
– A recent data brief from the American Hospital Association (AHA) and the ASTP/ONC examines the trends in predictive AI adoption, evaluation, and governance using data from 2023 and 2024. The findings highlight both the widespread adoption of this technology and the persistent challenges in its equitable implementation.
– The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare has seen significant growth over the past decade, with predictive AI becoming a key tool for improving outcomes and operational efficiency. Predictive AI uses machine learning to forecast future events, and in a hospital setting, this can include predicting patient readmission risks, facilitating scheduling, and simplifying billing procedures.
Predictive AI Adoption Trends
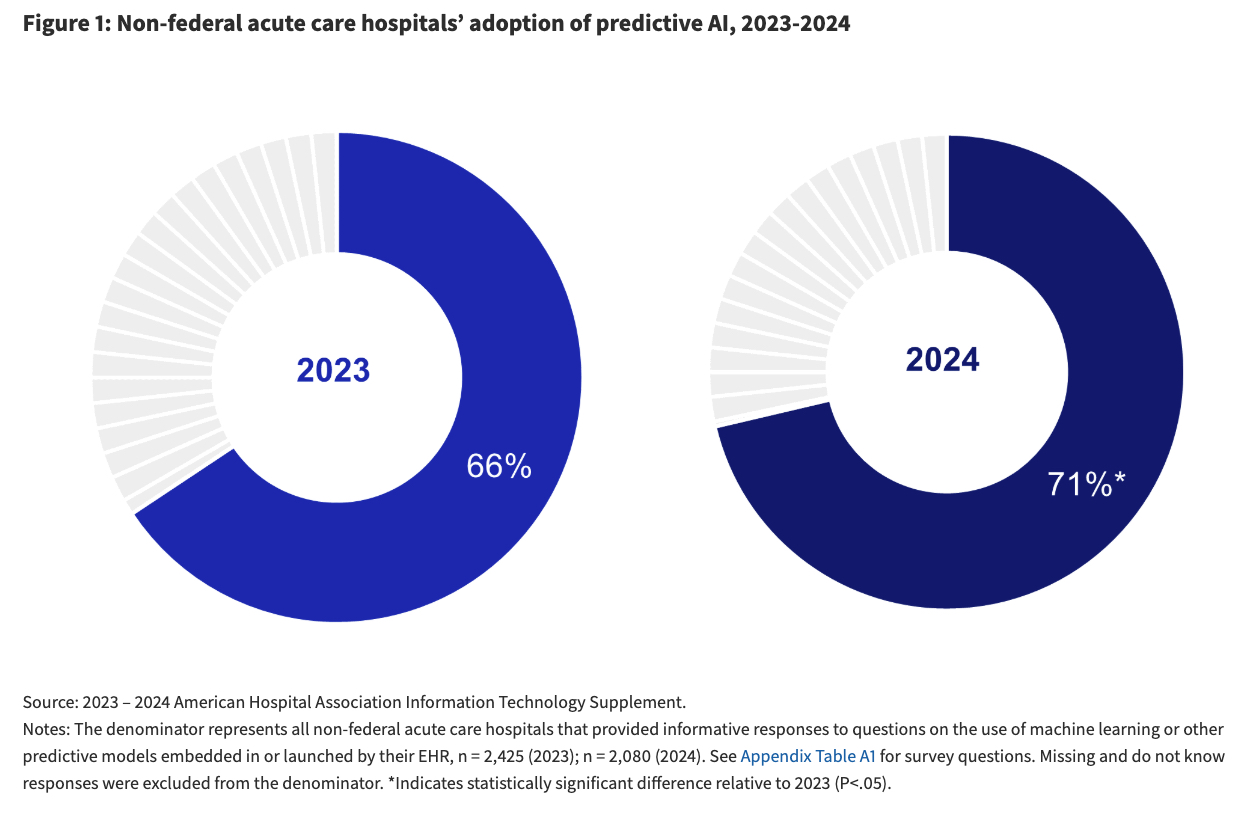
Predictive AI adoption is on the rise, with 71% of hospitals reporting its use in 2024, a notable increase from 66% in 2023. The most common application of this technology is to predict health trajectories or risks for inpatients. However, the fastest-growing use cases are administrative, with significant increases in using AI to simplify billing and facilitate scheduling.
While adoption is growing, a “digital divide” persists. The report indicates that small, rural, independent, and government-owned hospitals lag behind their larger, urban, and system-affiliated counterparts in adopting predictive AI. For instance, in 2024, 86% of multi-hospital system members used predictive AI, compared to only 37% of independent hospitals.
Hospitals are also sourcing their AI models from various places. In 2024, 80% of hospitals used predictive AI from their electronic health record (EHR) developer, while 52% used third-party developed AI and 50% used self-developed AI.
Evaluation and Governance of Predictive AI
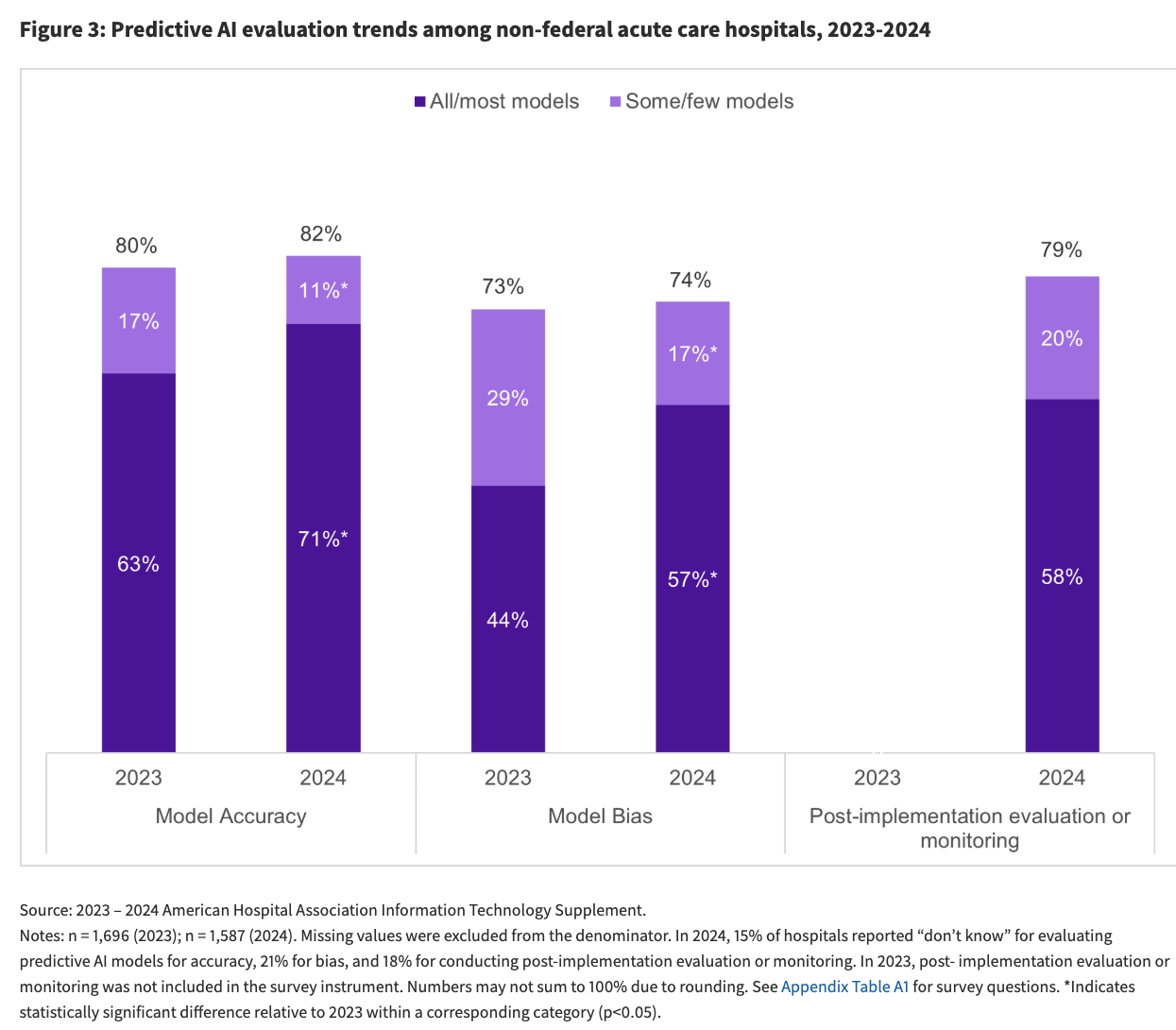
As predictive AI becomes more common, the importance of its evaluation and governance grows. The report reveals that most hospitals evaluate their AI models for both accuracy and bias. In 2024, 82% of hospitals evaluated for accuracy and 74% for bias. A growing number of hospitals are also evaluating all or most of their models for these factors.
The responsibility for evaluating these models is often shared among multiple entities within a hospital or health system. Three-quarters of hospitals reported that multiple entities were accountable for evaluating predictive AI in 2024, with a specific committee or task force being the most common entity cited (66%). Division or department leaders were also frequently mentioned as responsible parties (60%).
Future Outlook and Challenges
The report’s findings suggest an active and competitive market for AI tools, particularly for administrative tasks. However, while the use of predictive AI for administrative purposes is increasing rapidly, its use for clinical applications like recommending treatments or monitoring health remains low. This may be due to the higher risk of errors associated with clinical use.
For more information about the ASTP/ONC data brief, visit Hospital Trends in the Use, Evaluation, and Governance of Predictive AI, 2023-2024
