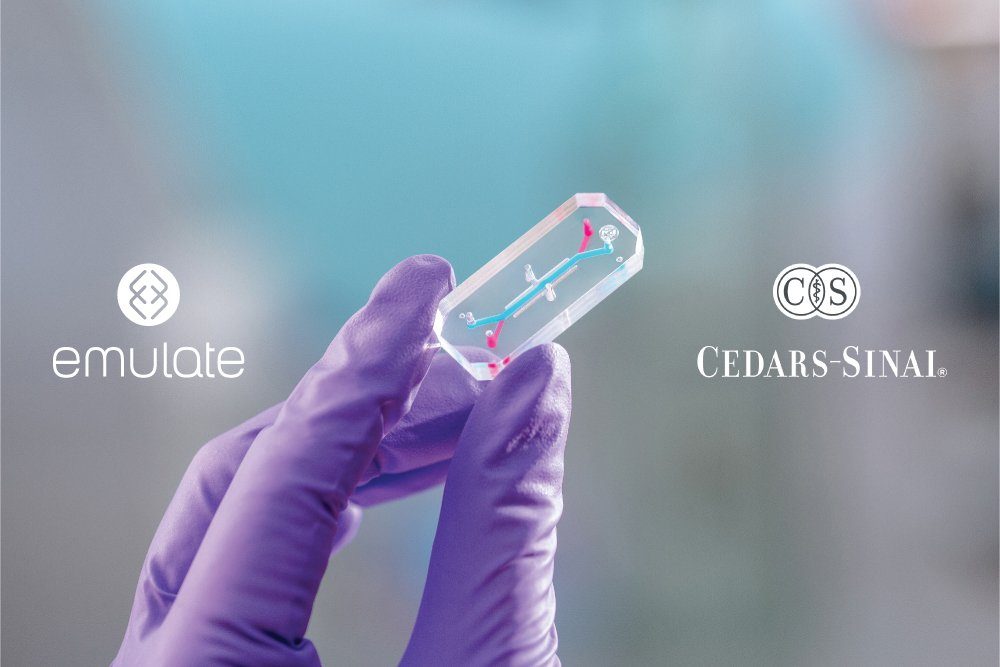
Scientists at Cedars-Sinai and Boston-based digital health startup Emulate are pioneering a Patient-on-a-Chip program to help predict which disease treatments would be most effective based on a patient’s genetic makeup and disease variant—a new approach to advance precision medicine.
Researchers know that people respond differently to foods, drugs, and chemicals. For example, a medication may be effective in one individual, while it makes another even more ill. Until now, we’ve had no way to test how a diet or a treatment plan would affect a person before administering it to them.
The collaboration leverages innovative stem cell science from the Cedars-Sinai Board of Governors Regenerative Medicine Institute and Emulate’s Human Emulation System, which uses Organs-on-Chips technology to re-create true-to-life biology outside the body. This technology creates an environment where the cells exhibit an unprecedented level of biological function, and provides control of complex human biology and disease mechanisms not possible with existing techniques.
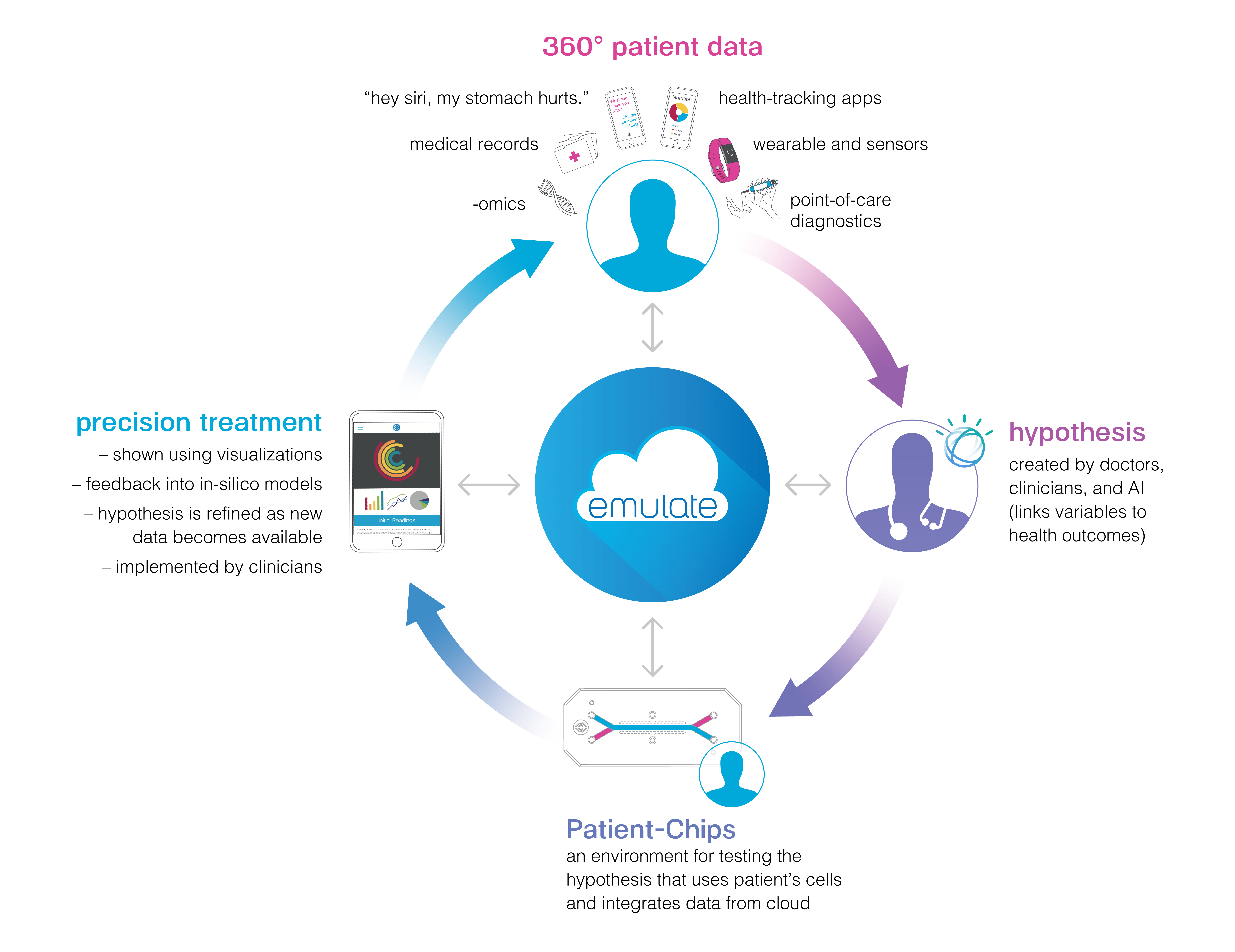
This Patient-on-a-Chip program holds the potential to advance the field of precision medicine and provide clinicians with a new system that more accurately predicts an individual’s response to foods, medicines, and chemicals.
The research points to a host of practical clinical applications that can benefit patients. By placing a patient’s cells in Organ-Chips and exposing those cells to a particular drug or series of drugs, clinicians could gain more accurate information about how that individual would respond to treatment, avoiding the risk of administering a drug that may cause harm or is ineffective and costly.
Emulate’s Human Emulation System — which is made up of Organs-on-Chips, instrumentation and software apps — re-creates the natural physiology cells experience within the body. Each chip, which is approximately the size of an AA battery, features tiny channels lined with tens of thousands of living human cells, recreating the smallest functional unit of an organ. Air and fluid, such as blood, can be passed through the chips, creating a micro-engineered environment that is a “home-away-from-home” for cells, where they behave just as they do in the body.
This project holds the potential to change the way diseases are treated. It will also change the way each of us understands and manages our own health by providing deeper insights into our own biology.
“By creating a personalized Patient-on-a-Chip, we can really begin to understand how diseases, medicines, chemicals and foods affect an individual’s health,” said Geraldine A. Hamilton, PhD, president and chief scientific officer of Emulate, Inc. in a statement. “The goal of Emulate working with Cedars-Sinai is to advance and qualify the system for new clinical applications and ultimately democratize the technology so that it can have broad impact on patient healthcare.”
In the future, a Patient-on-a-Chip also could be used to predict how a disease progresses in an individual, allowing for the design of personalized preventive medicine and treatment regimens to promote wellness and prevent disease, said Robert Barrett, PhD, an assistant professor of Medicine at Cedars-Sinai and senior author of the study in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology. Other applications include designing clinical trials to identify at-risk populations for adverse drug reactions.
