What You Should Know:
– Sophos’s State of Ransomware in Healthcare 2025 report reveals exploited vulnerabilities are now the leading technical cause of attacks (33%).
– The study highlights a sector becoming more resilient to encryption but facing soaring extortion-only attacks and high pressure on IT teams.
Root Causes Shift: Capacity Gaps and Exploited Vulnerabilities Lead
The latest Sophos study, based on the experiences of 292 healthcare providers, shows a significant shift in the technical and organizational root causes of ransomware attacks:
- Top Technical Cause: For the first time in three years, exploited vulnerabilities emerged as the most common technical root cause, used in 33% of incidents.
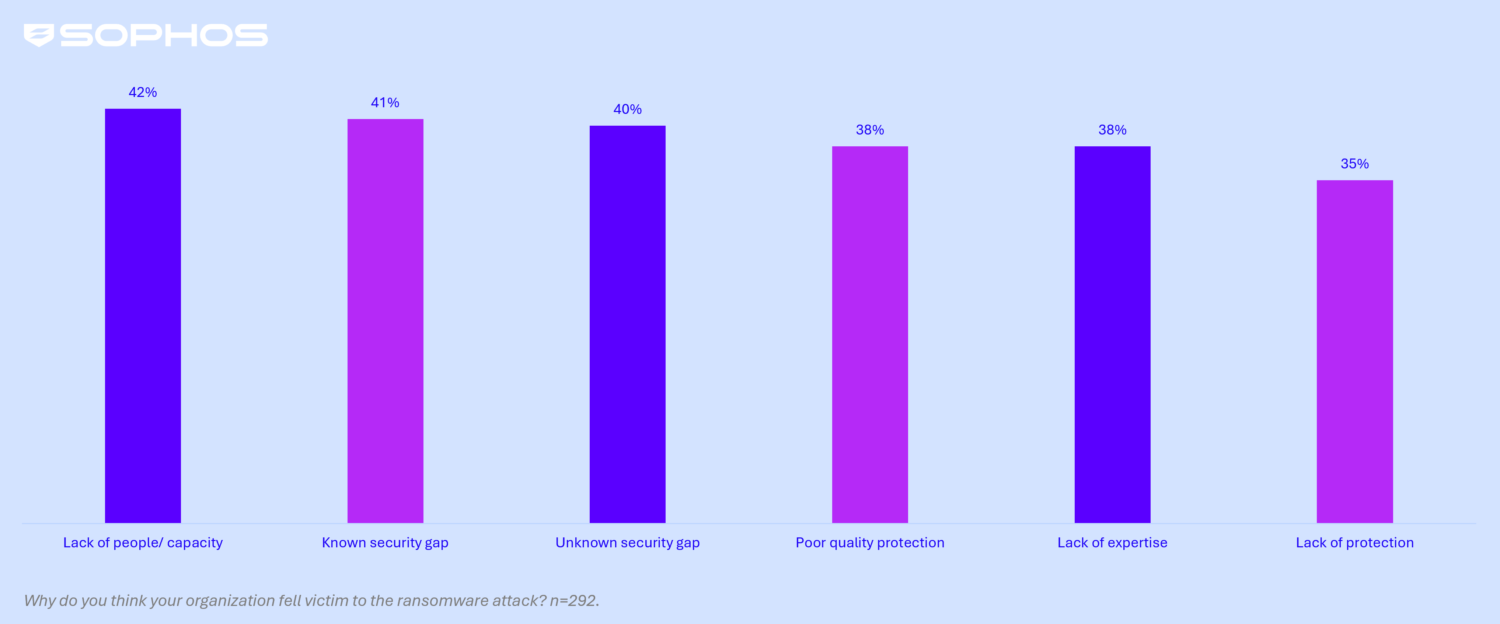
- Top Organizational Cause: The most common organizational factor contributing to attacks was a lack of people/capacity (i.e., insufficient cybersecurity experts monitoring systems), named by 42% of victims. This was closely followed by known security gaps (weaknesses organizations were aware of but had not addressed), cited in 41% of attacks.
Extortion Soars Despite Decline in Data Encryption
While healthcare organizations appear to be improving defenses against successful encryption, adversaries are adapting their tactics to exploit the sensitivity of medical data.
- Encryption Decline: The data encryption rate dropped to its lowest level in five years, with only 34% of attacks resulting in data encryption, down from a 74% peak in 2024.
- Extortion Triples: The proportion of healthcare providers hit by extortion-only attacks (where data was stolen but not encrypted) tripled to 12% of attacks in 2025.
Ransom Payments and Recovery Costs Plummet
The economics of healthcare ransomware shifted sharply, making the sector “a tougher environment” for cybercriminals to extract large payouts.
- Ransom Demands: The average (median) ransom demand plummeted 91% over the last year, from $4 million in 2024 to just $343K in 2025.
- Ransom Payments: The average (median) ransom paid dropped from $1.47 million to just $150K, the lowest payment reported across all surveyed industries.
- Recovery Costs: The mean cost of recovery (excluding ransom) fell by 60% to $1.02 million (down from $2.57 million in 2024).
Human Toll and Recovery Resilience
Every healthcare provider that had data encrypted reported direct repercussions for the IT/cybersecurity team.
- Pressure & Stress: 39% reported increased pressure from senior leaders, and 37% cited increased anxiety or stress about future attacks.
- Recovery Speed: Healthcare providers are recovering faster, with 58% recovered within a week in 2025, nearly triple the 21% reported in 2024.
- Backup Use Slips: Despite improved recovery speed, the use of backups to restore encrypted data has fallen to 51% (down from 72% in 2022)—suggesting possible weaknesses or a lack of confidence in backup resilience.
Click here for more information about the report
